What is The CIA TRIAD?
The CIA TRIAD Helps to Increase Security, Ensure Business Continuity and Protect an Organization’s Reputation
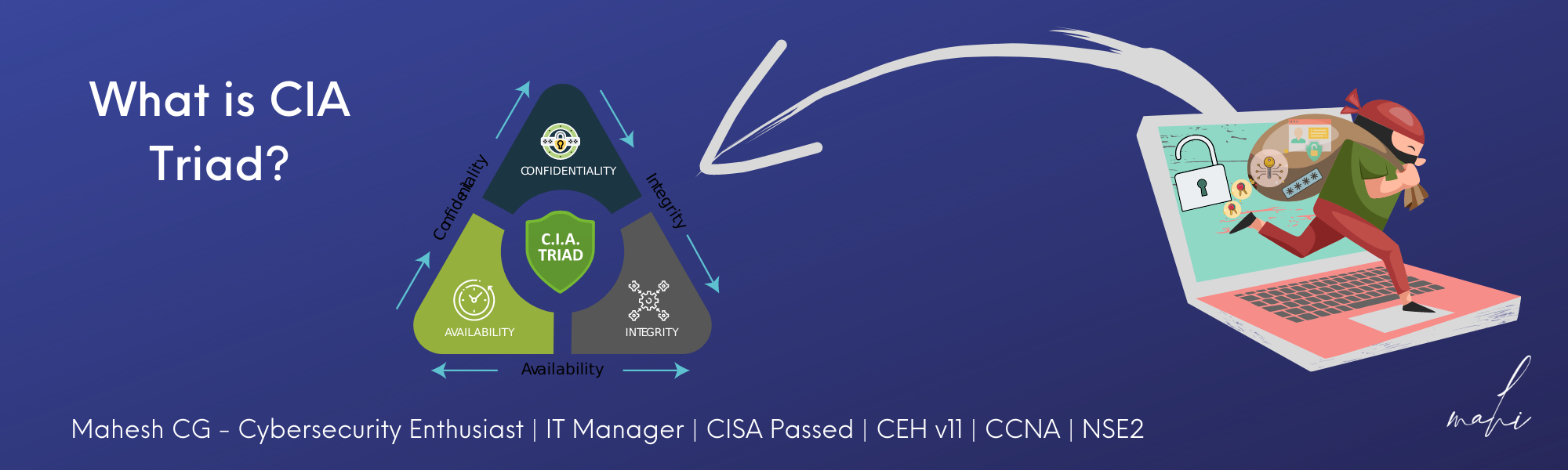
#Confidentiality, #integrity, and #availability — also known as the CIA triad—are often used to define the purpose of security. Using relevant and meaningful words, these terms help make security more understandable to management and users.
What is the #CIATRIAD?
Confidentiality
Confidentiality involves permitting authorized access to information while protecting it from improper disclosure.
Integrity
Integrity is the quality of information that ensures it remains complete, accurate, internally consistent, and useful for its intended purpose.
Availability
Availability means that systems and data are accessible at the time users need them.

Confidentiality
Ensuring data confidentiality can be difficult when many system users are guests or customers, and it is unknown if they are accessing the system from a compromised machine or vulnerable mobile application. Security professionals must regulate access—protect the data that needs protection yet permit access to #authorized individuals.
Personal Identifiable Information (#PII) is any information that, if released, could be used to identify a person. Other terms related to confidentiality include Protected Health Information (PHI), which includes an individual’s medical information, and Classified or Sensitive Information, which includes trade secrets and intellectual property.
One definition of information security is sensitivity, which is a measure of the importance assigned to information by its owner or the purpose of denoting its need for protection. Sensitive information is information that would cause harm if improperly disclosed (confidentiality) or modified (integrity). In many cases, sensitivity is related to the harm it could cause to external stakeholders, who are people or organizations that are not part of the organization that processes or uses the information.
Integrity
Integrity measures the degree to which something is whole and complete, internally consistent and correct. The concept of integrity applies to:
- Information or data
- Systems and processes for business operations
- Organizations
- People and their actions
#Dataintegrity is the assurance that data has not been altered in an unauthorized manner. This requires the protection of data in systems and during processing to ensure that it is free from improper modification, errors, or loss of information. Data integrity covers data in storage, during processing, and while in transit.
Information’s accuracy, consistency, and usefulness are important to all users, who rely on it to complete tasks. #Accuracy ensures that all related systems display and store the same information in the same way. Consistency helps ensure data integrity by ensuring that all instances of the data are identical in form, content, and, meaning.
System integrity refers to the maintenance of a known good configuration and expected operational function as the system processes information. Ensuring integrity begins with an awareness of the state, which is the system’s current condition. Specifically, this awareness concerns the ability to document and understand the state of data or a system at a certain point, creating a baseline. For example, a baseline can refer to the current state of the information—whether it is protected. The baseline establishes a starting point for determining what changes have occurred to determine whether any changes are unauthorized or intentional.
When baseline data are compared to current data, integrity can be ascertained. If the two matches, then the integrity of the data or the system is intact; if not, then the integrity of the data or the system has been compromised. Integrity is a primary factor in the reliability of information and systems.
The need to carry out information security measures is often dictated by laws and regulations. The need is also dictated by an organization’s need to access and use accurate, reliable information.
Availability
Availability can be defined as (1) timely and reliable access to #information and the ability to use it, and (2) timely and reliable access to data and information services.
The core concept of availability is that data is accessible to authorized users when and where it is needed in the form and format required. This does not mean that systems or data are available 100% of the time, but rather they meet requirements for a timely and reliable access.
Some systems and data are more critical than others, so the security professional must ensure appropriate availability levels. This requires consultation with the business to determine which systems are critical and how to protect them. Availability is often associated with the term criticality because it represents the importance an organization gives to data or an information system in performing its operations or achieving its mission.