Navigating NDMO’s Standards on Data Management of Saudi Arabia
In an increasingly data-driven world, the National Data Management Office (NDMO) of Saudi Arabia recognizes the critical importance of data management and personal data protection. As businesses and individuals generate and exchange vast amounts of information, safeguarding this sensitive data becomes paramount to maintaining trust, privacy, and security. For those operating within the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), adhering to the NDMO’s Standards, Data Management and Personal Data Protection Standards is crucial for effective navigation.
Understanding the NDMO’s Regulatory Framework
The National Data Management Office, established as part of Saudi Arabia’s commitment to advancing data-driven governance, plays a central role in developing and enforcing data management and personal data protection standards. The NDMO collaborates with various government entities to ensure a cohesive and comprehensive approach to data governance.
The primary legal instrument governing personal data protection in KSA is the Saudi Data Protection Law, enacted by the NDMO in collaboration with other government bodies. This law outlines the rights and responsibilities of data subjects, data controllers, and data processors, setting strict guidelines for processing and transferring personal data.
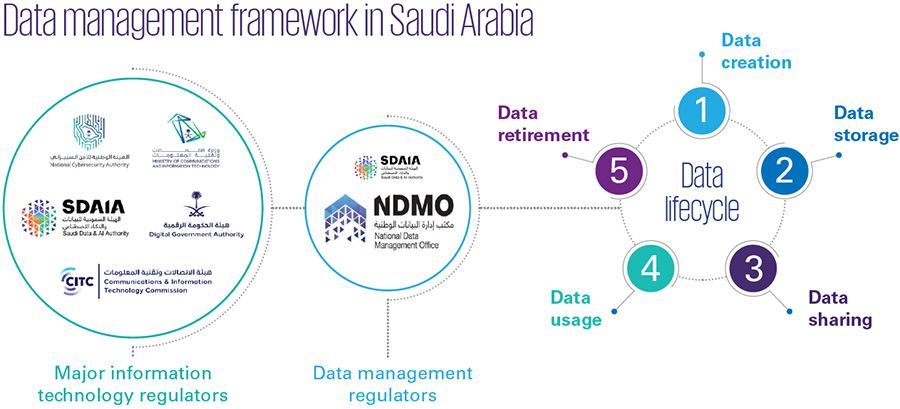
The Role of Data Management
Effective data management is foundational to ensuring compliance with the NDMO’s Data Management and Personal Data Protection Standards. It involves the collection, storage, processing, and disposal of data in a structured and secure manner, aligning with the following key principles:
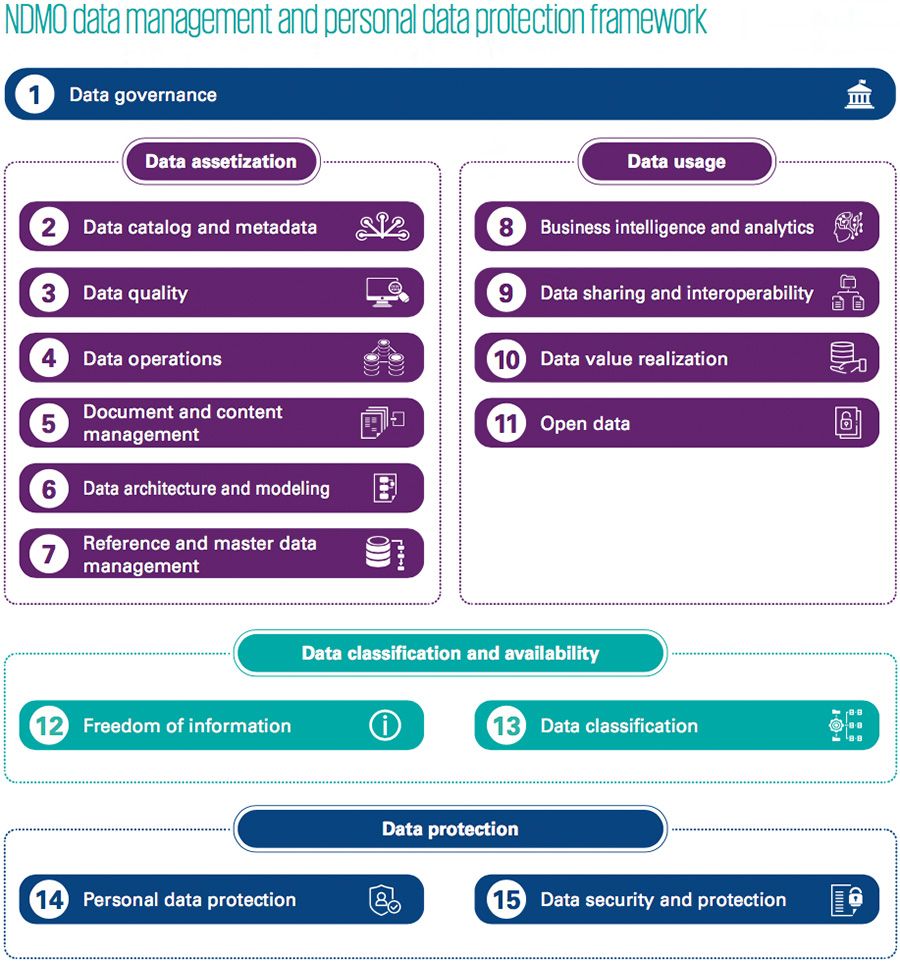
- Data Transparency and Accountability: Organizations must be transparent about their data practices and accountable for how they handle personal information.
- Lawful and Fair Processing: Data must be collected and processed lawfully, with explicit consent from individuals for specific purposes.
- Purpose Limitation: Data should only be used for the purposes for which it was collected, and further processing should be limited to compatible objectives.
- Data Minimization: Collecting and retaining only the minimum amount of personal data required for legitimate purposes reduces privacy risks.
- Data Security and Integrity: Robust security measures must be implemented to safeguard data from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction.
- Data Retention and Erasure: Personal data should be retained only for as long as necessary and disposed of securely when no longer required.
- Data Subject Rights: Individuals have the right to access, rectify, and delete their personal data, as well as the right to object to processing and data portability.
- Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA): Organizations must conduct DPIAs for high-risk data processing activities to assess and mitigate potential privacy risks.
- Data Breach Notification: In the event of a data breach, organizations must promptly notify the NDMO and affected individuals to take appropriate actions.
Ensuring Personal Data Protection
Individuals in Saudi Arabia have the right to exercise control over their personal data. Adhering to the NDMO’s guidelines, individuals can take the following steps to protect their data:
- Informed Consent: Always provide informed consent when sharing personal data with organizations, and ensure you understand how your data will be used.
- Data Access and Correction: Exercise your right to access the personal data held by organizations and request corrections if the information is inaccurate.
- Data Portability: When applicable, request your data in a commonly used and machine-readable format to facilitate data transfers.
- Opt-out Options: Take advantage of opt-out mechanisms provided by organizations for marketing communications or data sharing.
- Data Breach Awareness: Stay informed about data breaches and take appropriate actions if you suspect your data has been compromised.
Challenges and Future Outlook
As technology continues to evolve, the NDMO remains committed to updating and enhancing data management and personal data protection standards. The NDMO anticipates addressing challenges such as data localization, cross-border data transfers, and emerging technologies that may impact data privacy.
Conclusion
By adhering to the National Data Management Office’s Data Management and Personal Data Protection Standards, both businesses and individuals in Saudi Arabia can navigate the data landscape with confidence. Emphasizing ethical data practices and respecting individual privacy rights will help foster an environment of trust and security, ensuring that Saudi Arabia remains at the forefront of data-driven governance while safeguarding the privacy and rights of its citizens.




